摘要
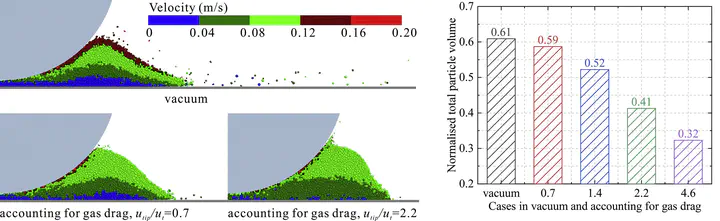
Powder spreading in Additive Manufacturing (AM) has been analysed extensively by the Discrete Element Method, but without considering the presence of ambient gas. For fine particles, as commonly used in AM, the gas drag could affect the quality of spread layer. Here, we consider the dynamics of powder spreading by a roller for a gas-atomised metal powder and analyse the combined effects of gas-particle interaction and interparticle adhesion on the particle flow in the heap and spread layer uniformity. In the presence of gas, the convection and circulation of particles within the heap are slowed down, and the heap repose angle becomes steeper. The amount of particles spread on the base is reduced, as compared to the case in which gas drag is not considered, but surprisingly particles with larger interparticle adhesion form a more uniform spread layer with larger total particle volume when gas drag is taken into account.